Trends and design research has developed as a pivotal practice in different industries, giving profitable experiences into customer preferences, market dynamics, and innovative advancements. This comprehensive article explores the concept of trends and design research, its importance, when and why it should be conducted, its pertinence in corporate settings, the process involved, the latest trends, and the application of modern tools and technologies. Moreover, we dig into a case ponder centered on the exterior design of refrigerators to provide a viable outline of the concepts examined.
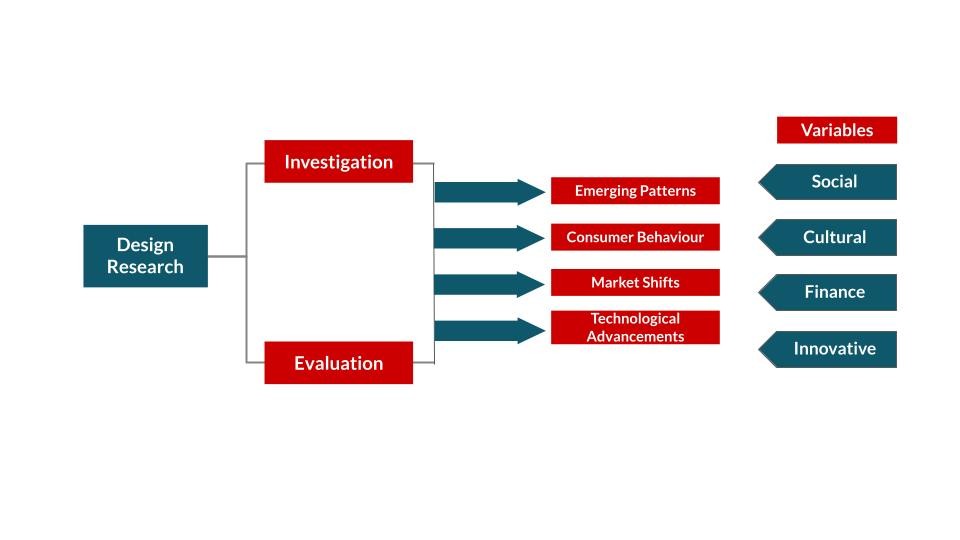
Trends and design research refers to a systematic investigation and examination of emerging patterns, customer behavior, market shifts, and technological advancements to illuminate design decisions and shape innovation techniques. It includes considering different variables, such as social, cultural, financial, and innovative changes, to distinguish opportunities and expect future needs.

Trends and design research should ideally be conducted during the early stages of the product development lifecycle. By understanding customers’ evolving needs and wants, businesses can adjust their design efforts with market demands, diminish risks, and pick up a competitive edge. In addition, it helps companies remain relevant, adjust to changing trends, and anticipate future market shifts.
Trends and design research finds application in different industries, but it is especially noticeable in customer goods, fashion, automotive, and technology sectors. Large organizations frequently depend on comprehensive research groups or external agencies to accumulate data, analyze trends, and interpret bits of knowledge into significant plan procedures. Small and medium-sized enterprises can benefit from joining drift research strategies into their design processes to drive development and meet customer expectations.
Product Design Process:
Designing a product typically involves several steps in the research and design process. While the exact approach can vary depending on the designer and the specific project, here are some common steps that designers may follow:

- Define the Problem: The first step is to clearly define the problem or need that the product is intended to address. This involves understanding the target audience, their requirements, and any existing challenges or limitations. For Example- “Identifying Consumer Preferences and Needs for a New Smart Home Refrigerator Design”.
- Conduct Research: Designers gather information through primary or secondary data collection method such as user interviews, surveys, market analysis, and competitive analysis. This helps them gain insights into user preferences, market trends, and existing solutions.

Some of the tools for Collecting Data are-
i. Qualitative Ethnographic Studies
ii. Quantitative Design Concept Research Tests
iii. Semiotics
- Generate Ideas: Based on the research findings, designers brainstorm and generate a wide range of ideas. This can involve sketching, creating concept boards, or using digital tools to explore different possibilities and approaches.
- Concept Development: From the generated ideas, designers select the most promising concepts and develop them further. This may involve creating detailed sketches, creating 3D models, or using computer-aided design (CAD) software to visualize the product.
- Prototype Creation: Once a concept is finalized, designers create prototypes to test and evaluate the product’s functionality, aesthetics, and user experience. Prototypes can range from simple models made with basic materials to fully functional and interactive prototypes.
- User Testing: Designers conduct user testing sessions where potential users interact with the prototypes. This allows designers to gather feedback, observe user behaviour, and identify areas for improvement. Iterative testing and refinement are often performed to enhance the product’s usability and appeal.
- Iterative Design: Based on the feedback from user testing, designers refine and iterate on the design, making necessary adjustments and enhancements. This may involve modifying the product’s features, ergonomics, materials, or aesthetics to better align with user needs and preferences.
- Finalize Design: Once the iterative design process is complete, designers finalize the product design. This involves creating detailed technical specifications, engineering drawings, and preparing the design for manufacturing.
- Production: Designers collaborate with manufacturers or production teams to bring the product design to life. They work on selecting appropriate materials, manufacturing processes, and ensuring the product is manufactured to meet quality standards.
- Launch and Evaluation: After production, the product is launched in the market. Designers may continue to gather feedback from users, monitor performance, and make further refinements based on real-world usage and customer feedback.
Process of Trends in Design Research:
The process of identifying and incorporating trends in research design involves several steps. Here is a general outline of the process:
- Literature Review: Conduct a thorough review of the existing literature in your field of study. Identify recent publications, research articles, and academic journals that discuss emerging trends and advancements in research design. This step will help you understand the current state of research and the areas where innovative approaches are being used.
- Engage with Peers and Experts: Connect with other researchers and experts in your field, either through professional networks or online communities. Engage in discussions, ask questions, and seek their opinions on emerging trends in research design. Collaborating with experienced researchers can provide valuable insights and help you stay updated with the latest developments.
- Follow Specialized Journals and Websites: Subscribe to specialized journals and websites that focus on research methodology and design. These sources often publish articles and papers highlighting innovative research methodologies and design trends. Regularly reviewing these publications will keep you informed about the latest practices in your field.
- Consult Methodology Experts: If possible, consult with methodological experts or research design consultants who specialize in your area of study. These professionals have in-depth knowledge of research methodologies and can guide you on incorporating the most appropriate and effective design trends into your research.
- Cross industry trend identification: Cross-industry trend identification in research design refers to the process of recognizing and incorporating relevant trends from different industries into the design of research studies. This approach allows researchers to gain insights and inspiration from various sectors, which can enhance the robustness and applicability of their research findings.
- Identifying Mega and Micro Trends/ Shifts: Identifying mega and micro trends/shifts is an essential task for businesses and individuals seeking to stay ahead in an ever-changing world. Below are some examples of mega and micro trends in respect to Refrigeration business-
i. Mega Trends:
Ø Energy Efficiency
Ø Smart Technology Integration
ii. Micro Trends/Shifts:
Ø Food Preservation Technologies
Ø Customization and Personalization
- Lifestyle trends: Lifestyle trends can significantly impact research design, as they provide insights into consumer behavior’s, preferences, and values. By understanding and incorporating lifestyle trends into research design, businesses can gather more relevant and actionable data.
Remember, while it is important to be aware of emerging trends, it is equally important to critically evaluate their suitability for your specific research objectives and context.
New Tools and Technologies:
Advancements in technology have altogether affected patterns and design research. A few tools and methodologies are presently available to upgrade the research process, such as:

- Big Data Analytics and Machine Learning Algorithms for Trend Prediction: Big data analytics involves collecting and analysing large volumes of data to extract valuable insights. By analysing vast amounts of data, designers can make informed decisions about the design direction, product features, and market positioning to meet the evolving needs of their target audience.
- Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) for Immersive Design Experiences: VR and AR allow designers to create immersive experiences during the design process, providing a realistic sense of scale, form, and spatial relationships. AR overlays digital elements onto the real world, allowing designers to see how their designs would interact with the physical environment. By using VR and AR, designers can gain a deeper understanding of their designs, identify potential issues, and refine them before physical prototyping.
- Social Media Monitoring and Opinion Analysis for Real-time Customer Experiences: Social media platforms are valuable sources of real-time feedback and customer insights, allowing designers to gain a better understanding of customer experiences, preferences, and expectations. This information can help guide design decisions, identify areas for improvement, and provide valuable input for future product development.
- Design Thinking Techniques to Foster Innovation and Empathy-driven Design: Design thinking is a problem-solving approach that emphasizes empathy, collaboration, and iterative prototyping. It helps designers understand user needs, uncover insights, and generate innovative solutions. Techniques such as user interviews, personas, journey mapping, and brainstorming sessions help foster creativity, collaboration, and innovation.
- Rapid Prototyping and 3D Printing for Iterative Design Cycles: Rapid prototyping techniques, such as 3D printing, enable designers to quickly create physical prototypes of their designs, allowing them to test and evaluate the form, functionality, and user experience. This allows designers to iterate on their designs more efficiently, making improvements based on real-world testing and user feedback.
Case Study: Refrigerator (Exterior Design):

Let us investigate a case study focused on the exterior design of refrigerators. In this scenario, a leading appliance manufacturer wanted to patch up their refrigerator designs to align with changing customer preferences and the evolving kitchen aesthetics.

- Research phase: The company-initiated trend research to understand the emerging trends in kitchen design, consumer expectations, and the role of refrigerators as a focal point. They conducted consumer surveys, analyzed market reports, and studied kitchen design blogs and magazines.
- Analysis phase: The research findings revealed that minimalistic and sleek designs were gaining popularity, with a focus on integration with the overall kitchen environment. Sustainability and energy efficiency were also identified as significant factors influencing consumer choices.
- Synthesis and design phase: Based on the insights, the design team proposed new refrigerator designs that incorporated minimalistic aesthetics, sleek finishes, and smart technology features. Attention was given to reducing energy consumption, utilizing sustainable materials, and integrating the refrigerator seamlessly into the kitchen space.
- Implementation and evaluation phase: The new refrigerator designs were prototyped and tested with consumers for feedback and usability. Iterative refinements were made based on the user insights and evaluated against the initial research objectives.
Trends and design research play a significant role in driving innovation, shaping design methodologies, and staying ahead in a rapidly evolving market. By understanding customer preferences, market dynamics, and developing technologies, businesses can create products and experiences that resonate with their target group of audience. Through precise research, analysis, and application of trends, companies can design products that are not only aesthetically appealing but also meet the functional and passionate needs of customers. With the help of modern tools and technologies, the research process is becoming more productive and accurate, empowering designers and businesses to create transformative solutions.